By Susan Shea
One summer, I took a nature drawing class, and we hiked up Stowe Pinnacle to sketch in the cool, mountain forest. I chose to draw a big yellow birch that had established itself on the steep slope. For a couple of hours, I stared at the base of the tree, trying to capture its intricate detail: the way the trunk leaned to the right and its large, supporting roots spread over the ground; the variable colors, patterns, and textures of its bark; a hole at the base that might be home to a mouse or chipmunk. I wondered how old the tree was and what it had witnessed in its lifetime from its perch on the mountainside.
Yellow birch is one of the dominant trees of our northern hardwood forest, along with sugar maple and beech, and it also is common at higher elevations — up to about 2,900 feet — where it often grows beside red spruce. Most specimens are easy to identify by their glossy, silver-yellow bark, which breaks into strips that shred and curl at the edges. Yellow birch is longer-lived than most birch species — it can live to be 200 to 300 years old and grow to over 4 feet in diameter. As a yellow birch ages, its bark develops large, rough plates, and these gnarled, old-growth giants aren’t easily recognizable as the same species.
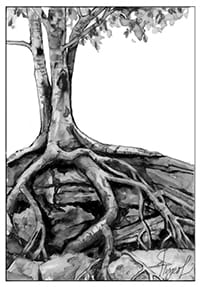
This birch prefers cool, moist, nutrient-rich soils. It tends to grow on the rootballs of fallen trees, from cracks in boulders, and on decaying stumps and mossy logs. Because seedling roots cannot pierce hard surfaces, including the compacted leaf litter of the forest floor, they often first spread laterally over a stump or rock, then downwards into the soil. I marvel at yellow birches growing beside mountain trails, their roots wrapped around boulders. I have also seen mature trees standing on stilt-like roots — what remains after the original log or stump they began life on rots away.
Because its seedlings don’t survive in deep shade, yellow birch benefits when natural disturbances such as wind, ice or snow loading, insects, or disease cause other trees to fall, creating small gaps in the forest canopy. Due to the low odds of landing on a good site, seed predation, and other factors, only about 1% of yellow birch seeds successfully grow into seedlings.
In spring, the tree’s long, drooping catkins are covered with yellow pollen. These are the male flowers. Before the leaves come out, small female flowers emerge from buds on the same tree and are pollinated by the wind. Later, the leaf buds open, unfurling oval, yellow-green leaves with pointed tips and double-toothed edges.
During summer, the female flowers develop into fruits — small, cone-like structures bearing seeds. In autumn, the seeds — tiny, winged nutlets — ripen. Winter winds slowly disperse the seeds, scattering them across the snow, where they are an important food source for songbirds, including chickadees and redpolls. Ruffed grouse and red squirrels also consume these seeds, as well as the buds and catkins. Deer, moose, and snowshoe hare browse seedlings, leaves, and stems. In spring, yellow-bellied sapsuckers drill holes in the bark of yellow birch and feed on sap and the insects attracted to it. Returning hummingbirds are drawn to the sap wells created by this woodpecker.
Humans use yellow birch trees for a variety of products. Syrup can be made from the sweet sap, and tea from the wintergreen-flavored twigs. The red-brown to cream-colored wood is close-grained, hard, and strong. This valuable wood is widely used for veneer and plywood and popular for interior doors, cabinets, trim, furniture, and woodenware. Its graceful form and attractive bark make the yellow birch a good native tree to plant in the yard, if you have a suitable site.
Susan Shea is a naturalist, writer, and conservationist who lives in Brookfield, Vermont. Illustration by Adelaide Murphy Tyrol. The Outside Story is assigned and edited by Northern Woodlands magazine and sponsored by the Wellborn Ecology Fund of the New Hampshire Charitable Foundation: nhcf.org.



