The Vermont Fish & Wildlife Dept. won a $106,256 competitive grant from the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service to take advantage of groundbreaking new data that will help conservation planners protect plants, animals and their habitats in the face of climate change.
Vermont conservation design is a science-based assessment of Vermont’s ecologically functional landscape that helps guide strategic fish and wildlife conservation. “With this grant, we are excited to fine-tune our assessment to better identify lands and waters that contribute to Vermont’s healthy environment with climate change in mind,” said Director of Wildlife Mark Scott.
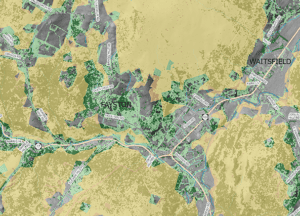
Map shows 2016 LIDAR-derived tree cover (light and dark green) overlaid with 2011 habitat blocks (orange) which highlights the opportunities to improve Vermont Conservation Design with new data that account for connecting landscapes.
First released in 2015, Vermont conservation design maps the habitat needed to ensure Vermont’s wildlife remains healthy and abundant. Six years later, new state-wide “LIDAR” data from the Vermont Center for Geographic Information provide an opportunity to upgrade this conservation tool.
LIDAR, the acronym for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that uses aircraft-mounted laser scanners and a global positioning system to map landscape texture, giving researchers a more accurate understanding of land cover. It provides 400 times higher resolution than any previous landcover data.
The new data will reveal critical details for wildlife movement and ecological connections, like hedgerows through fields and forest edges close to roads. These connections allow animals to move from one habitat block to the next as they adjust their ranges to climate change.
“These very detailed land cover maps will help us find the places where wildlife, such as black bears and bobcats, can travel between large patches of forest,” says Jens Hilke, a conservation planner at Vermont Fish & Wildlife. “It is critical that wildlife have the ability to move around the state and beyond, especially as climate change pushes plants and animals into new habitats.”
Federal support for this project highlights the department’s leadership in science-based conservation. “The competitive state wildlife grants provide a proactive, collaborative and innovative mechanism for addressing significant threats to our nation’s cherished wildlife and their habitats,” said U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Principal Deputy Director Martha Williams.
“This grant enables us to enhance and accelerate our work with new science, so that priority species from moose and northern long-eared bats to native bees and rare plants remain healthy and able to adapt to climate change in Vermont and beyond,” Scott added.




